Body mass index (BMI) is a device that medical care suppliers use to gauge how much muscle to fat ratio by utilizing your level and weight estimations. It can assist with surveying risk factors for specific medical issue. The BMI isn’t generally a precise portrayal of body heftiness.
Body mass index (BMI) is a clinical screening instrument that actions the proportion of your level to your weight to gauge how much muscle to fat ratio you have. Medical services suppliers work out BMI by involving weight in kilograms (kg) isolated by the square of level in meters (m2).
In a great many people, BMI connects to muscle versus fat — the higher the number, the more muscle versus fat you might have —but it’s not accurate in some cases. BMI alone doesn’t analyze wellbeing. Medical care suppliers use BMI and different instruments and tests to evaluate somebody’s wellbeing status and dangers.
High muscle versus fat might prompt coronary illness, stroke and Type 2 diabetes. Low muscle to fat ratio might be connected with lack of healthy sustenance. A perfect proportion of muscle to fat ratio assists nutrients and minerals with getting into your body. It likewise gives a wellspring of energy to your body, keeps up with internal heat level and safeguards your organs.
You shouldn’t utilize the standard BMI diagram to assess a kid’s or alternately teen’s weight. Converse with your kid’s medical services supplier about the ideal weight territory for their age and level.
Also Read: What is Omega-3 Supplement : Uses and Health benefits
Table of Contents
How to Calculate BMI?
Medical care suppliers use BMI to assist with diagnosing weight types and as an evaluating device for specific medical issue.
Diagnosing weight types with BMI
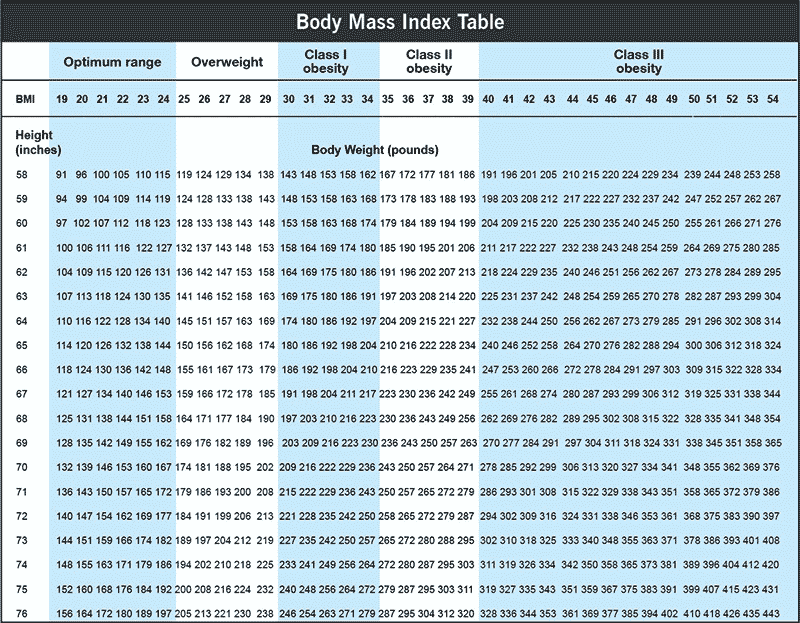
As a general rule, the accompanying BMI ranges (in kg/m2) group different weight types:
- Underweight: Less than 18.5.
- Optimum range: 18.5 to 24.9.
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9.
- Class I obesity: 30 to 34.9.
- Class II obesity: 35 to 39.9.
- Class III obesity: More than 40.
BMI isn’t the main instrument suppliers use to characterize weight types. Different devices include:
- Estimating abdomen circuit.
- Estimating skin thickness involving skinfold calipers in specific region of your body, like the rear of your upper arms and under your shoulder bones.
- DEXA scan and air removal plethysmography (ADP) — these are utilized once in a while.
Also Read: 7 Tips to Increase Hair Faster and Stronger
Healthy BMI:
The ideal reach for a solid BMI is viewed as 18.5 to 24.9.
It’s memorable’s essential that body largeness isn’t the main determiner of generally speaking wellbeing. A few different variables, for example, hereditary qualities, movement level, smoking cigarettes or utilizing tobacco, drinking liquor and psychological Health conditions all influence your general wellbeing and your probability of fostering specific ailments.
What are the limitations of BMI?
The standard BMI Chart has limits because of multiple factors. Along these lines, it’s vital to not put a lot of accentuation on your BMI.
Despite the fact that the BMI Chart can be incorrect for specific individuals, medical care suppliers actually use it since it’s the speediest device for evaluating an individual’s assessed muscle versus fat sum.
Limitations of using BMI to help diagnose weight types:

Also Read: 5 Benefits Of Using Olive Oil For Cooking
The standard BMI has limits concerning diagnosing weight types, including:
- BMI doesn’t separate between lean weight (the heaviness of all that in your body with the exception of endlessly fat mass. Along these lines, an individual can have a high BMI (by being solid) yet at the same time have an extremely low fat mass as well as the other way around.
- Similar BMI outline is utilized for adults assigned male at birth (AMAB) and adults assigned female at birth (AFAB) despite the fact that grown-ups AFAB ordinarily have more muscle to fat ratio than grown-ups AMAB.
- The BMI graph hasn’t been adapted to the rising typical grown-up level throughout the long term.
You shouldn’t utilize the standard BMI chart to evaluate how much muscle to fat ratio of the following populaces:
- Athletes and bodybuilders.
- Children and teenagers.
- Pregnant people.
- People over the age of 65.
- People who have muscle atrophy (wasting) due to medical conditions.
Limitations of using BMI as an evaluating instrument for medical issue
The BMI as an evaluating device for surveying the gamble of specific medical issue, like Sort 2 diabetes and coronary illness, has a few restrictions, including:
- The BMI doesn’t gauge the area or conveyance of muscle versus fat. This is an issue since overabundance fat collection in specific region of your body, like in your gut (midsection), is related with a higher gamble of ailments than overabundance fat gathering in different region of your body, like in your thighs.
- The connection among BMI and pace of death frequently doesn’t represent such factors as family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease and high cholesterol (dyslipidemia); familial longevity (average lifespan); or family history of cancer.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Body mass index (BMI) is a speedy instrument that medical services suppliers can use to survey your gamble for specific medical issue. In any case, BMI isn’t generally a precise estimation of body heftiness and isn’t the sole determiner of your overall wellbeing. On the off chance that you have any different kinds of feedback about your weight or your gamble for fostering specific medical issue, like coronary illness, converse with your medical services supplier. They’re accessible to help.

